Data quality
The data quality dashboard allows for analyzing the changes in missing and unseen values over time. Here is our guide explaining how to use the data quality dashboard:
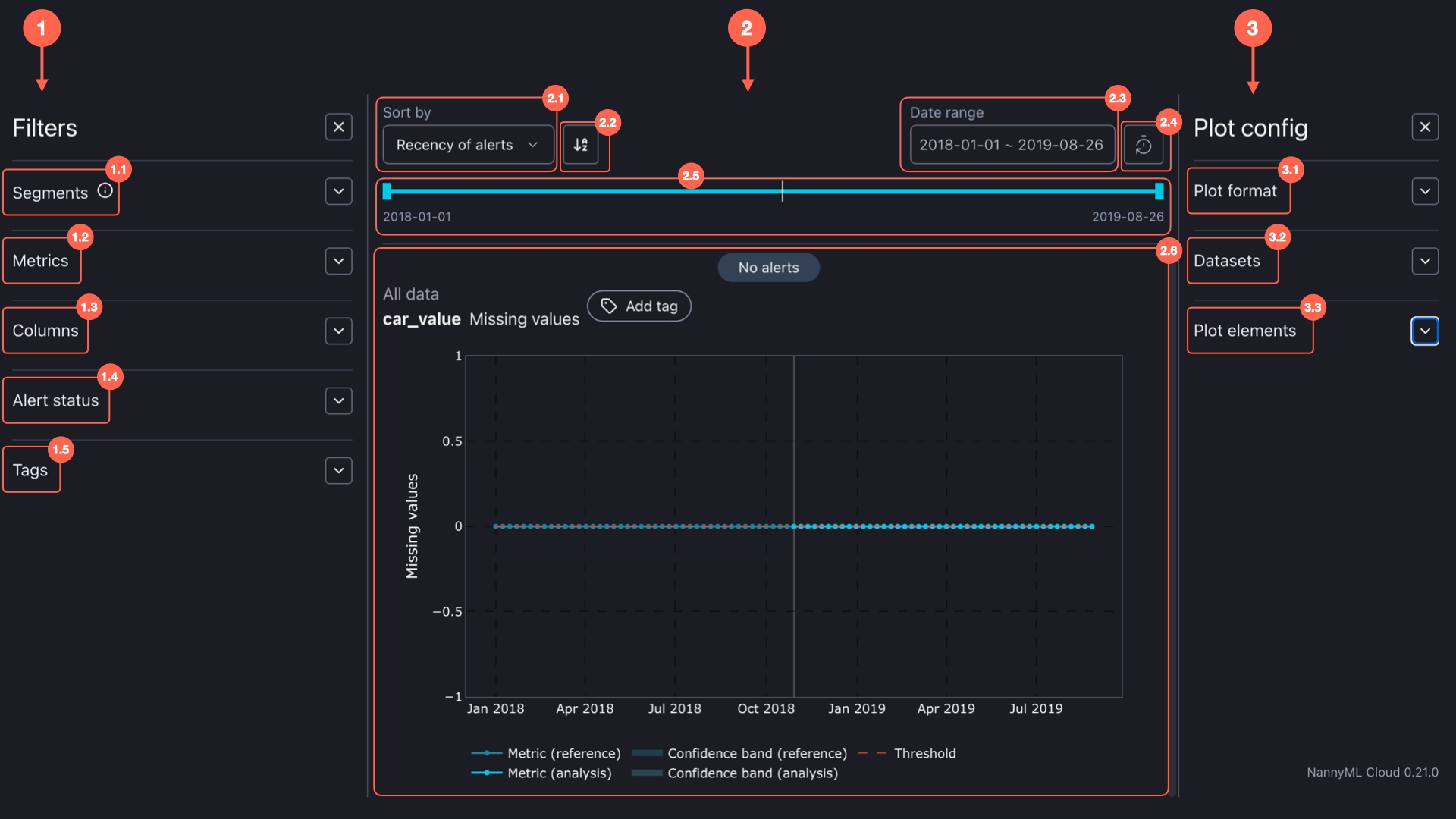
There are three main components of the Data quality dashboard:
1. Filters
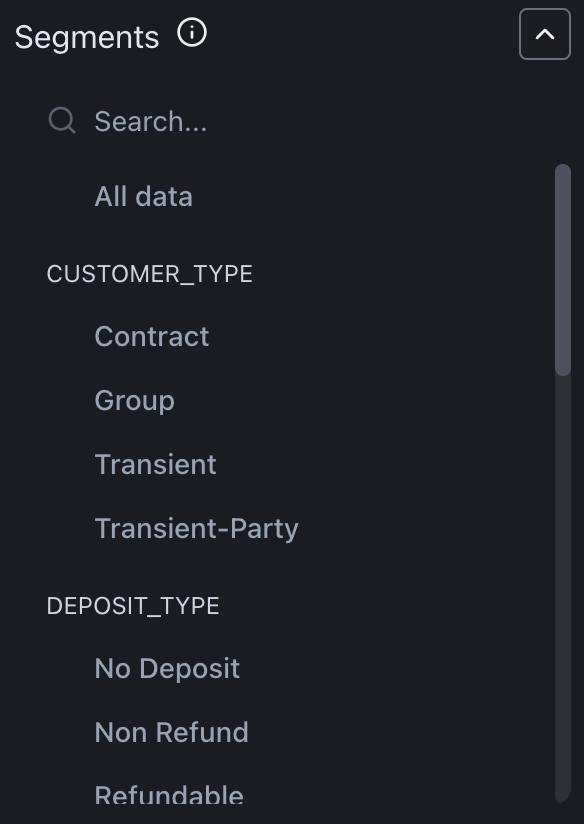
Segmentation allows you to split your data into groups and analyze them separately.
For a given model, each of the columns that are selected for segmentation during configuration or in the model settings appears under the segmentation filter. Segments are then created for each of the distinct values within that column.
In the filter section, you can select the segments you want to see visualized. You can also select All data to visualize results for the entire dataset.
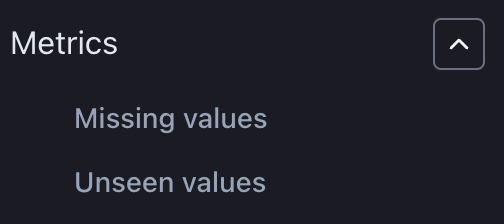
Filter which data quality metrics you want to see. Data quality metrics that are not calculated are not visible under the filter. Selecting which data quality metrics you want to calculate can be done under model settings.
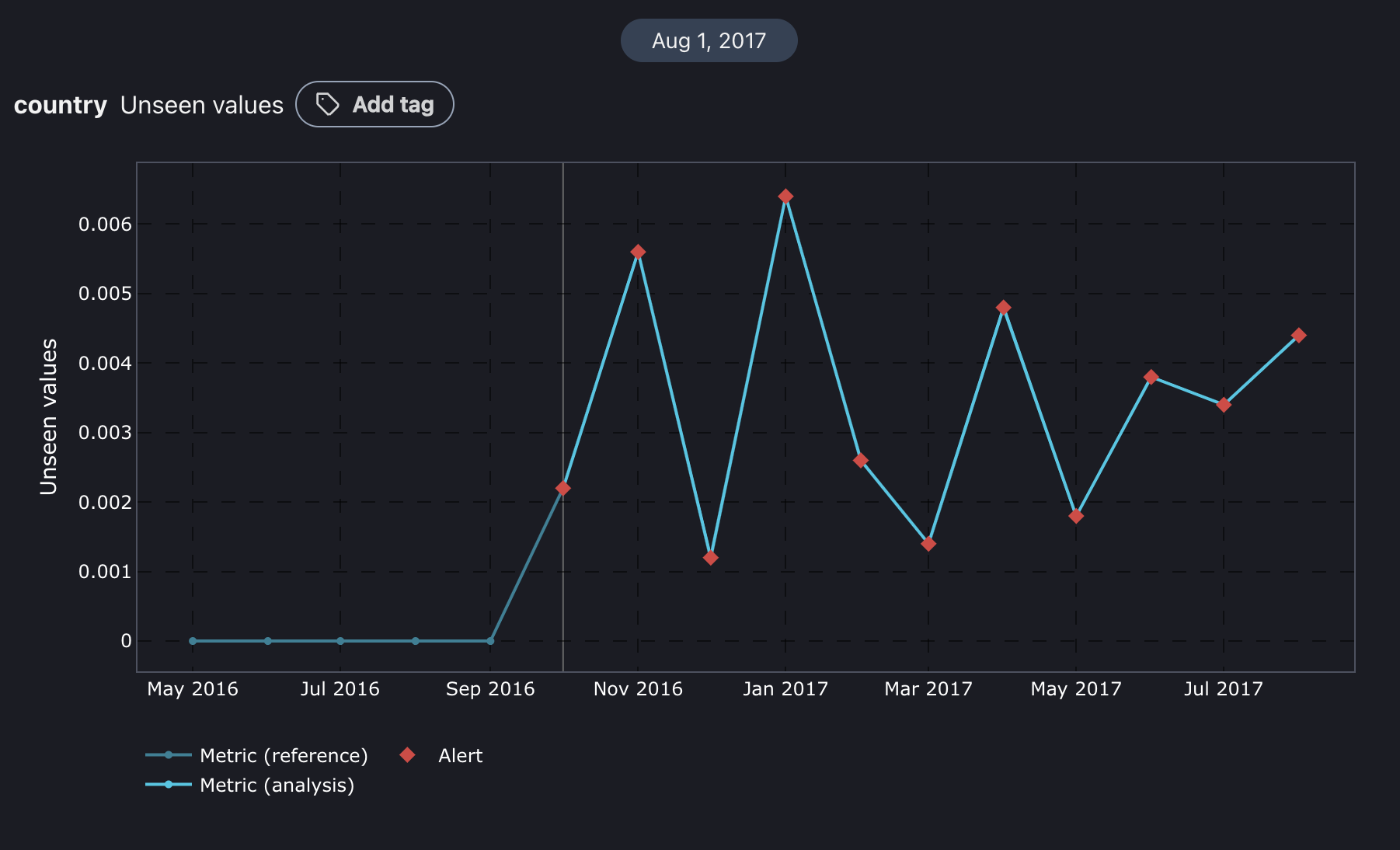
Note that unseen values do not apply to continuous columns. It is typically used to assess if new categories are appearing on which the model was not trained.
Filter the resulting charts by the columns you want to see.
Note that the data quality metrics can also be applied to the model output and the target, not just the features.
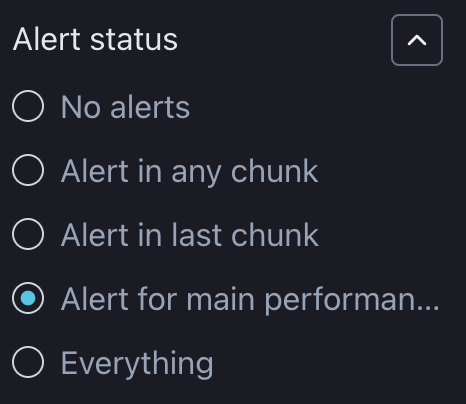
Select which metrics to display depending on whether there are alerts in the last chunk, alerts in the previous chunks, or no alerts at all, or include all charts regardless of when and if any alerts occurred.
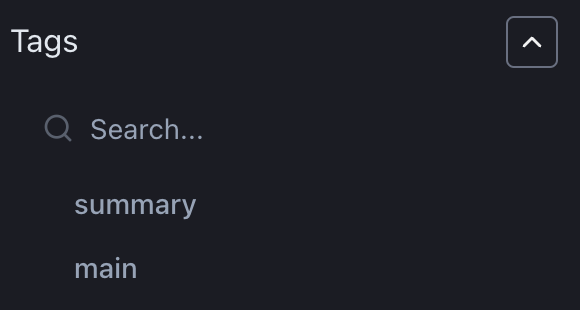
Filter charts by the previously specified tags.
2. Visualisations
You can change the order of charts based on the metric name, number, or recency of the alerts.
For all sorting methods, the icons shown below toggle between ascending and descending order. The icon displayed depends on the selected sorting method.
Column Name and Method Name: The icon toggles between alphabetical order and reverse alphabetical order. The default mode is alphabetical order.
Nr of Alerts: The icon toggles between ascending and descending order based on the number of alerts. The default mode displays plots with the most alerts first.
Recency of Alerts: The icon toggles between showing newer alerts first and older alerts first. The default mode shows the most recent alerts first.


You can select a specific period of interest which applies to all charts.
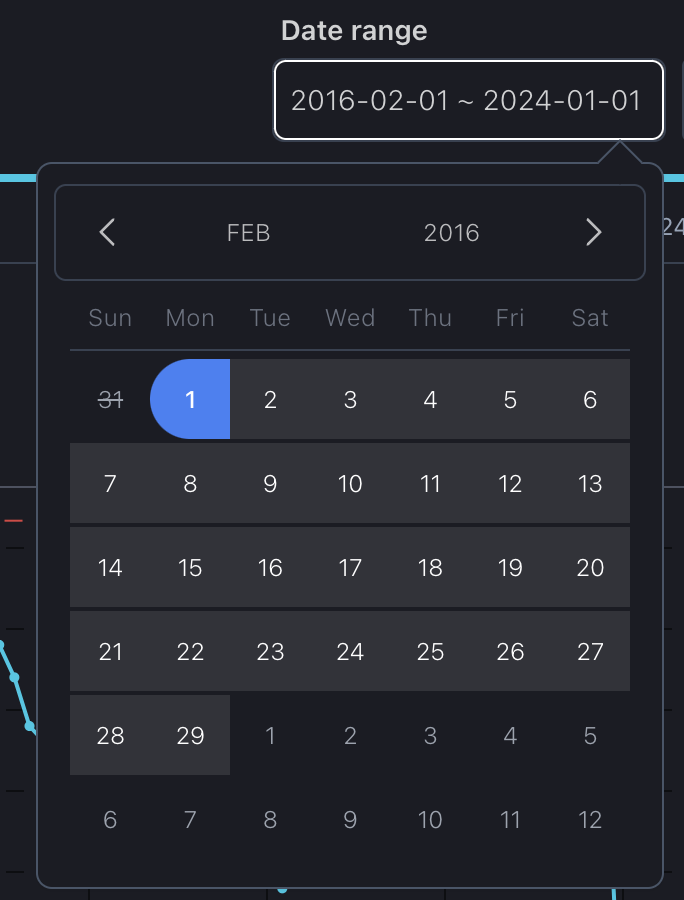
To reset a previously set date period, whether using the date range or slider, simply press the "Reset" button.
Similar to selecting a date range, you can choose a specific period of interest by simply moving the date slider.

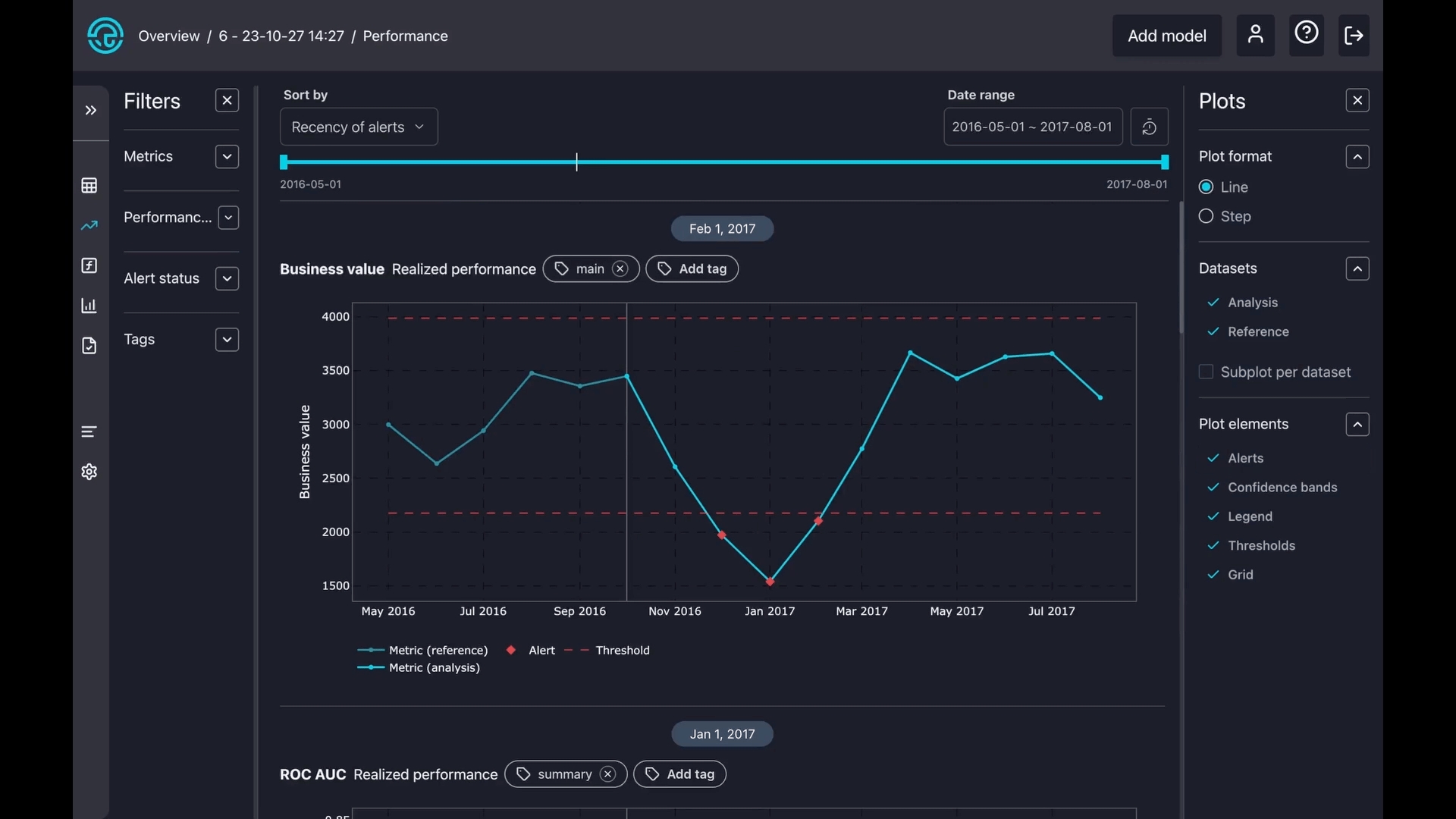
The charts are interactive; you can hover over them for more details. Red squares signal alerts, and the blue line represents the metric in the reference period. The light blue line indicates the metric during the analysis period.
You can also zoom in on any part of a chart. Simply press and hold your mouse button, then draw a square over your area of interest. To reset the zoom, just double-click on the chart.
3. Plot config
There are two types of plot formats: line and step. A line plot smoothly connects points with straight lines to show trends, while a step plot uses sharp vertical and horizontal lines to show exact changes between points clearly.
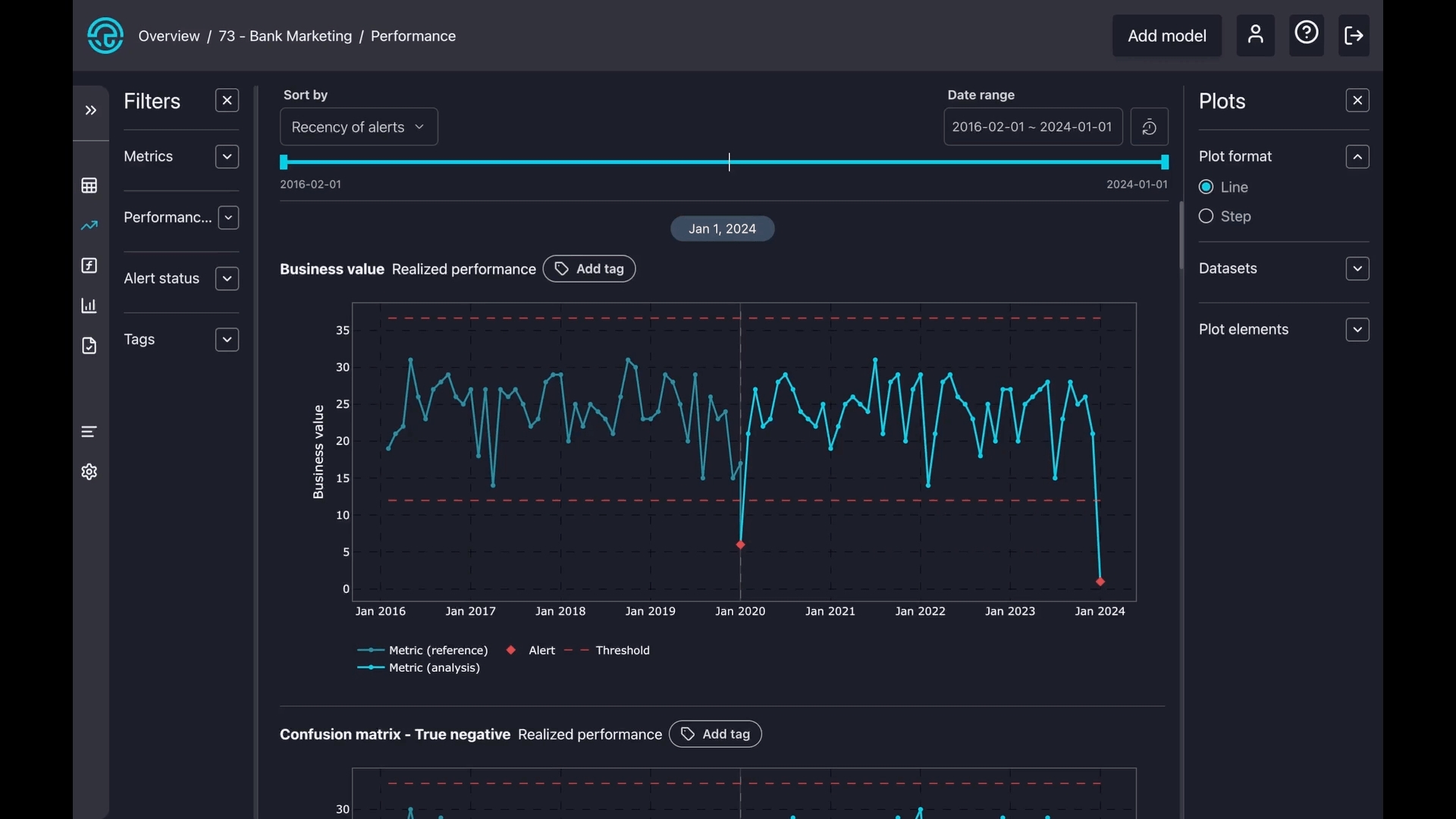
Select datasets to zoom in on reference, analysis, or create a separate subplot for both.
Toggle on or off some components on the charts, like alerts, confidence bands, thresholds, and legends.